What is securities? – Securities have nothing to do with protecting your belongings, placing a CCTV camera at your home, or preventing hacking in a cyber space. In the world of investing and finance, securities are the financial instruments that have some value and can be traded between different parties.
Broadly speaking, security refers to a fungible, or negotiable financial instrument that is intangible in its appearance. Due to its intangibility, it can only represent its ownership in the form of stocks, bonds, options, mutual funds or exchange-traded funds. It doesn’t represent ownership in the form of any tangible asset like car, land or any other possession for that matter.
ALSO READ: What are the Impacts of a Recession on the Stock Market?
What Types of Securities Are There?
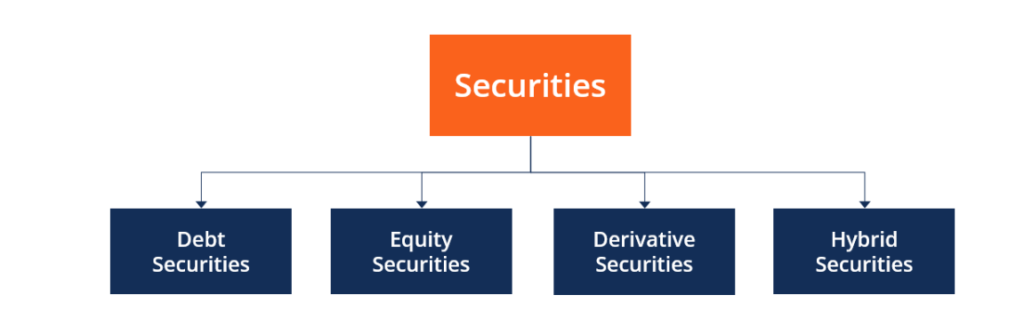
Securities can be defined into four broad categories; equity securities, debt securities, derivative securities and last but not the least, hybrid form of securities.
Equity Securities
An equity security represents the ownership held in a company by the public as its shareholders. In other words, it is an investment in the business of a particular firm and its equity to become the shareholder or part owner of that entity.
Equity securities holders are not entitled to regular inflows of income – although it does pay dividends, but neither they are paid in regular intervals, nor do they have any fixed amount or ratio. So the main source of income for the equity holders is the profit they receive from selling the shares of that company.
Once they sell their shares to someone else, if sold at a higher value than the purchasing value, will yield a profit, termed as capital gains. Similarly, if sold in a loss, it will be termed as capital loss.
Another important aspect of the equity based securities is the right of ownership a shareholder gets when he acquires that shares. This means that those shares represent the ownership of a shareholder in the business proportionate to the number of shares acquired by them.
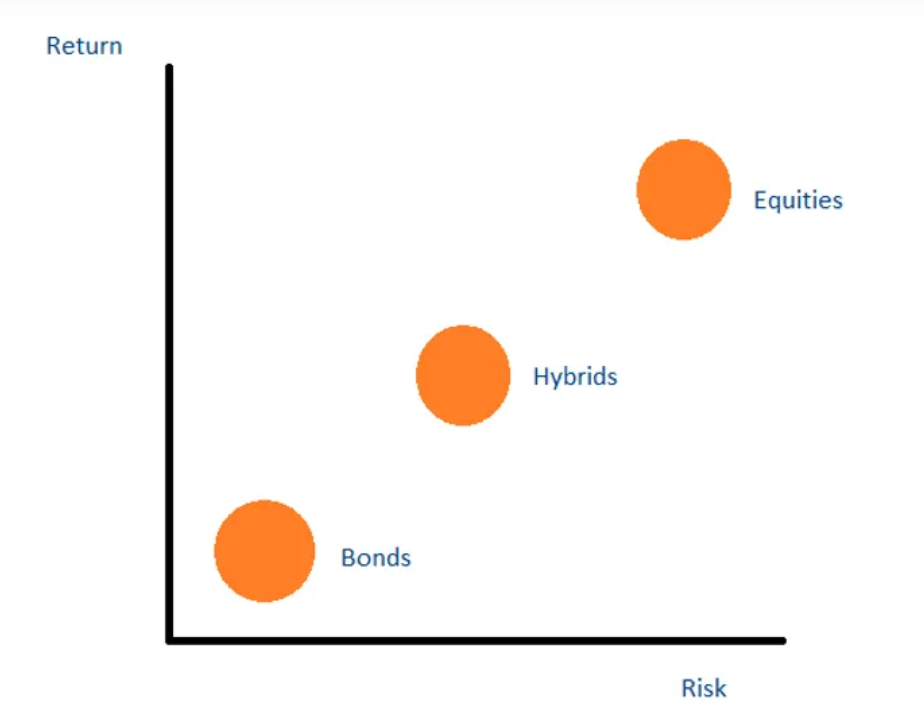
The main advantage associated with the equity securities is that you usually grow with the company you have invested in, as they usually pay out dividends while earning higher profits, in addition to the capital gain earned on value increment of the investment.
However, a big disadvantage associated with this type of security is that during a phase of turbulence, or bankruptcy; equity security holders are the last ones entitled to receive any residual amount after payments to the lenders.
DONT FORGET: How does rising interest rates affect the stock market?
Debt Securities
Debt securities, or commonly known as fixed-income securities, provides its owners the right to receive fixed income at regular intervals in the form of coupon or interest payments and the complete principal amount at the end of the maturity.
It distinguishes itself from the equity securities as it has an element of known profits to it and is considered rather less risky than equity based securities. Moreover, it also contains a maturity date, usually a few months to 20 years, whereas there is nothing of this sort in equity securities.
Debt securities can include corporate and government bonds, collateralized securities, or certificates of deposits. They are typically issued for a fixed term upon which it will be redeemed by the issuer.
The main advantages associated with the debt securities is that it has a fixed term or maturity assigned to it which reduces the element of perpetual risk involved in transactions. Moreover, the instrument holder is also entitled to fixed and regular payments along with the principal amount redeemed at maturity, regardless of the financial position of the issuer.
A major disadvantage of debt-based securities is that you do not have a say in the governance of the firm as you don’t get any voting rights as is the case with equity securities.
In a debt based security, the interest rate you will receive depends upon the credit history, solvency, liquidity and track record of the issuer entity. The higher the risk of default of the issuer firm, the higher interest rates an issuer would be required to pay in lieu of that risk.
MUST READ: Are Annuities Affected By the Stock Market?
Derivative Securities
Derivative securities are a little more complex than the previous ones. They are the financial instruments whose worth depends upon some kind of asset, like stocks, currencies, bonds, market indexes or commodities.
The main purpose of using derivative securities is to take systematic and unsystematic risks into consideration, while transacting and reducing that risk. This can be done by insuring against unwanted price movements, creating an environment of market speculation or gaining access to hard to reach asset classes.
In older days, derivatives were used to ensure balanced exchange rates during international trade, as traders needed an accounting system to lock different currencies at different exchange rates.
However, in recent times its use has taken a turn in investments and profit earning tools. Derivative securities can be divided into four main categories:
Futures:
As explained by the name itself, futures are the types of contracts or agreement between two parties for the purchase and deliverance of an asset at an already agreed price in the future. Futures are traded on an exchange with standardized forms of contracts.
Forwards:
A forward contract is somewhat similar to the futures in its characteristics; however, it doesn’t trade on any exchange. It is traded over the counter and the parties involved need to determine size, terms & conditions and settlement process for the derivatives.
Another difference is that it involves the risk of bankruptcy in losing the financial position, as there is limited extent of backing and if one party gets bankrupt, then the other party will not be able to protect its rights.
Options:
Options are also somewhat similar to the futures contract as it also involves transacting on a predetermined price at a future date. However, it doesn’t require you to perform any action of buying or selling.
The most commonly traded options are the call options, which gains value if the underlying asset appreciates in value, and the put options, which gains value when the underlying asset loses its value.
Swaps:
They are completely different forms of derivatives, as it involves the swapping of one type of cash flow with another. For example, an interest rate swap allows the trader to convert from a fixed interest rate to a variable interest rate loan.
POPULAR PICKS: What are the points in the stock market? – A complete guide for Beginners
Hybrid Securities
As the name suggests, this type of security has some of the characteristics of both, the debt and equity based securities. Numerous organizations and financial institutions use hybrid securities to borrow money.
It is similar to bonds as it carries a fixed or a floating interest payment until a certain time in future. The frequency of interest payments in hybrid securities is not guaranteed.
Some of the commonly used examples of hybrid securities include convertible bonds, equity warrants, and preference shares. Convertible bonds can be converted into the shares of a company. Equity warrants are issued by the company itself, giving the right to the shareholder to buy the shares at a specific price and within a certain timeframe. Preference shares have their dividend and principal payment prioritized over normal shares.
Hybrid securities are one of the most complex financial products, as many experienced investors and even the institutional investors struggle to understand the value and risks involved in trading them.
The conclusion
Securities, though are complex products, but they are of profound value to the financial markets and the financial environment as many institutional investors invest in this asset class. Moreover, it is als necessary for the markets as it is an important tool to raise capital from the public.